
Did you know that certain nonprofits can legally opt out of paying state unemployment taxes? Do you understand who is benefiting from this tax exemption law? In this article, Jon Pratt, Executive Director at Minnesota Council of Nonprofits, discusses the benefits of nonprofit tax exemption and recent tax activity statistics.
It is important to understand that a tax-exempt status only exempts a nonprofit from paying tax on income that is generated from activities that are specifically related to the purpose for which the group was created. Nonprofits are not alone in benefiting from this exemption—by allowing more dollars to funnel back into the very missions that started nonprofit organizations—communities worldwide are reaping the benefits of endless services being offered by these 501(c)(3) organizations.
Jon Pratt explains, “Even though nonprofits are sometimes considered to be an essentially “tax-free” sector of the economy, they clearly have deep involvement on both sides of the ledger: as a tax expenditure, in the sense of forgone revenue, and as taxpayers and tax collectors, making substantial contributions to government revenues through tax collection from nonprofit employees and activities.”
To learn more about the national value of charitable nonprofit benefits and obligations, read the full article here.
Article provided by Jon Pratt, Executive Director at Minnesota Council of Nonprofits, Co-Director of GrantAdvisor and UST board member

Question:One of our employees has asked to bring her 16-year-old daughter to work so she can volunteer for school credits. Can we allow this?
Answer: It depends. Under the federal Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), employees may not volunteer services to for-profit private sector employers. However, private employers may have trainees or students in the workplace under the School-to-Work program (STW) or an internship program.
If you want to allow your employee’s daughter to do work for you as an intern, you will need to classify her as such. Keep in mind internships can be either paid or unpaid. The United States Department of Labor (DOL) uses six criteria to determine whether an internship is exempt from the minimum wage and overtime requirements of the FLSA (meaning the internship may be unpaid). Under the DOL test, for an intern to be exempt from the minimum wage and overtime requirements, all of the following must be true:
For more information on the DOL six-factor test, see Fact Sheet #71: Internship Programs Under the Fair Labor Standards Act. Note that the 2nd Circuit (Connecticut, New York, and Vermont) and the 11th Circuit (Alabama, Georgia, and Florida) do not use the DOL six-factor test but instead use the “primary beneficiary test.” Under the primary beneficiary test, a court determines whether the employer or worker benefits more from the internship. If the employer benefits more, the worker is properly classified as an “employee” and is entitled to minimum wage and overtime. If the individual benefits more, he or she is properly classified as an unpaid intern or trainee and exempted from the minimum wage and overtime requirements (nonemployees). As unpaid internships have proven to be a litigious area of employment law, seek legal guidance before electing to not pay an intern.
Finally, beyond these exceptions to the FLSA, if your employee’s minor 16-year-old daughter will be doing any work for the company not as an intern, she must obtain a work permit, must be paid at least the applicable minimum wage, and is entitled to the protections afforded other employees. You’ll also need to consider that each state has its own laws governing the employment of minors. Check here to review the laws applicable to your state.
Q&A provided by ThinkHR, powering the UST HR Workplace for nonprofit HR teams. Have HR questions? Sign your nonprofit up for a free 30-day trial here.

March resulted in positive job growth with employers adding an additional 196,000 jobs with considerable job gains in the healthcare and professional/technical services. Employment growth averaged 180,000 per month in the first quarter compared to the 223,000 per month in 2018 and this month the unemployment rate remained the same at 3.8 percent. The number of unemployed persons remained unchanged at 6.2 million.
During the month of March, the number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) showed minimal to no change at 130 million and accounts for 21.1 percent of those unemployed. With the labor force participation rate at 63 percent, it showed slight change over the course of the month and little movement on net over the past 12 months. In addition, the number of persons employed part-time for economic reasons (referred to as involuntary part-time workers) showed small changes at 4.5 million in March. To explain, these are individuals who would have preferred to have full-time employment and were working part-time due to their hours being reduced or unable to find full-time employment.
Job gains occurred in health care adding 49,000 jobs and 398,000 over the past 12 months. This growth increased employment in ambulatory health care services (+27,000), hospitals (+14,000) and nursing/ residential care facilities (+9,000). In addition, there was a significate increase in the professional and technical services of 34,000 and 311,000 over the past 12 months. The growth increased employment in design and related services (+12,000), architectural engineering services (+6,000) and management and technical consulting services (+6,000). Employment also showed an upward trend in food services and drinking (+27,000) as well in construction (+16,000) with an increase of 246,000 over the past 12 months.
In March, average hourly earnings for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls increased by 4 cents to $27.70, following a 10-cent gain in February. Over the past 12 months, average hourly earnings have increased by 3.2 percent. Average hourly earnings of private-sector production and nonsupervisory employees increased by 6 cents to $23.24 in March.
With the revisions of both the January and February’s job reports, the number of jobs went from +311,000 to +312,000 for January and +20,000 to +30,000 for February – combined there were 14,000 more jobs than previously reported. These changes show a continual growth in employment and the upward trend of different sectors benefiting from this positive job growth.

Employing the third largest workforce with the third largest employee payroll, the nonprofit sector is quickly gaining momentum in the work arena. Work for Good recently released a new eBook, the 2019 Nonprofit Salary Report for California, based on results from an extensive survey of nonprofit professionals in the state. This eBook delivers comprehensive sector salary benchmarking based on nearly 10,000 positions at nonprofit organizations in the state of California. Those are impressive statistics and this report breaks down those numbers for you—helping in your quest for greater impact and organizational excellence. Download your copy today!

Question: We received a request from the State Department of Labor, Division of Research and Statistics, to provide information for “Occupational Employment Statistics Report in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Labor.” Is our participation mandatory or required?
Answer: Your state department of labor has asked you to participate in the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Current Employment Statistics survey. Providing information is voluntary under federal law and is mandatory under state law only in North Carolina, Oregon, and South Carolina.
The report is based on a sample of 390,000 business establishments nationwide. The survey produces monthly estimates of employment, hours, and earnings for the nation, states, and major metropolitan areas. Preliminary national estimates for a given reference month are typically published on the first Friday of the following month, in conjunction with data derived from a separate survey of households, the Current Population Survey. See the Bureau of Labor Statistics Current Population Survey page and the Current Employment Statistics page for more information.
Although voluntary in most states, employers are encouraged to complete and submit the report accordingly. No penalties exist for those who choose not to report in states where participation is not mandatory.
Q&A provided by ThinkHR, powering the UST HR Workplace for nonprofit HR teams. Have HR questions? Sign your nonprofit up for a free 30-day trial here.

From 2007 to 2016, the nonprofit sector experienced substantial growth in employment and a range of industries reaped the benefits of this growth. During this time, nonprofits surpassed the for-profit sector in employment growth with a 16.7 percent increase compared to the 4.6 percent increase in the for-profit sector. With consistent resilience and very little recognition for these efforts, nonprofits had the ability to employ nearly twice as many workers as construction, finance, insurance and transportation.
When looking at how nonprofit employment is distributed across a variety of industries, it can be helpful to see which industries benefited from this growth. Hospitals came in at the highest with 34 percent of the total, along with other health care sectors (e.g., nursing homes and health clinics) at another 21 percent. Next, is education with 14 percent of nonprofit employment then social services with 12 percent. An interesting point made in The 2019 Nonprofit Employment Report is “within the industries noted above, nonprofit workers tend to out-earn for-profit workers” and an example of this is, “an average nonprofit worker in ambulatory health earns $1,364 a week versus $1,101 for a person employed in the same industry by a for-profit firm. That is a 24 percent nonprofit wage advantage. In the social assistance sector, the nonprofit wage advantage is a stunning 55 percent.”
While nonprofits are less impacted by recessions than for-profit firms, they still face other obstacles that are unavoidable. For-profits continue to make advancements and are outpace nonprofits in a number of the traditional nonprofit sectors, such as nursing and residential care field, hospital field, social assistance; to name a few. For-profits also continue to grow in the private sector and while nonprofits are growing in the service(s) sectors, they are growing faster than the economy can accommodate.
With the nonprofit sector continuing to show resilience while battling with the many economic pressures and in constant competition with the for-profit sector, the nonprofit sector continues to push on. However, attention needs to be given to the many factors that impact the future of nonprofit business models.

Most people spend the majority of their weekday hours getting ready for work, commuting to and from work and actively working. As a standard rule of thumb, we make it a priority to ensure we live in a safe environment at home–free from negative energy. But what about our work environment? How can we ensure the environment is safe there as well?
Some typical issues encountered in the workplace that can be bothersome include poor lighting and fluctuating temperatures, but other issues that are surprisingly common that can seriously undermine employee health are workplace bullying and sexual harassment. These types of behavior can have an extremely negative impact on the well-being, productivity, and health of everyone in the office, not just those directly involved. Creating a safe work environment means focusing on culture and eliminating harmful behavior.
Many people think these negative behaviors stop once the graduation caps have been tossed in the air. Unfortunately, bullying is a common problem that can occur in any setting involving a large group of people, and the workplace is no exception. With digital tools like office chatrooms, texting, and email, there are more ways than ever for abusers to target others. Workplace harassment can encompass a number of harmful behaviors, including threats, humiliation, sabotage, and intimidation. It is this repeated harassment that can affect the victim’s ability to concentrate and/or feel safe at work.
One of the biggest problems with workplace harassment is that many people don’t recognize it when they see it. Not all harassment is obvious. Sometimes, it’s subtle and the effects build up over time. Alternatively, the abuser may be using digital tools that no one else can see rather than engaging in inappropriate behavior in front of others. In other cases, people that are witness to bullying may not feel safe coming forward. Research indicates that a shocking 37% of workers in the United States have been directly bullied in the workplace. When you factor in the people who witnesses bullying, the number reaches 49%. All in all, even if a person hasn’t been bullied on the job, chances are they know someone who has. Because of the negative consequences, these behaviors are a leading contributor of toxic work environments around the country.
Not only does workplace harassment cause victims to lose their confidence and experience increased stress, it can also lead to poor productivity, illness, and possibly, to the person quitting. A toxic culture increases turnover rates and can even open up companies to legal trouble if allowed to continue.
Workplace harassment is a serious issue and should therefore, be handled promptly. Not only can it lead to mental and physical health problems for your employees, it can also impact your bottom line and even hurt your reputation. Eliminating toxic behavior through education and awareness are key when it comes to ending workplace harassment of any kind and of the utmost importance in creating a safe and healthy work environment. Mandatory trainings for managers and employees, strict policies on harassment, and other safeguards can help ensure a safe and healthy environment for all.
This article was created in collaboration with Quinn Cooley of DC Scholarships.


As a nonprofit manager, it is important to be able to give constructive feedback effectively to your employees. Being able to share and receive feedback is vital to self- improvement. Examples of how to give constructive feedback include, discussing appropriate behaviors, asking questions, creating an action plan together and building trust, to name a few. On the other hand, there are a number of ways that your feedback could cause more harm than good.
Listed below are five bad habits your nonprofit organization should avoid when giving constructive feedback:
1) Waiting for the annual performance review to give feedback – This method can cause confusion and make things more challenging to work through. Waiting too long to provide feedback could make people feel caught off guard or defensive rather than being open to having a productive conversation.
2) Not providing specific examples – Concepts like “be more of a team player,” “be more professional” or “show more initiative” do not typically sink in without the use of specific examples to illustrate them. Labels without examples can leave people feeling at a loss of how to go about making changes because they are unsure of what you’re looking for. Make sure to be specific with your feedback.
3) Lack of preparation – Making an assessment or judgment call prior to gathering all the facts and examining the logic of your assessment, can lead to a very negative outcome. Situations like these could lead to resentment or loss of respect for the manager. Every statement you share, whether it be criticism or praise, should be backed up with specific details.
4) Making an assumption of how to praise an employee – A natural tactic is to praise an employee the same way you like to be praised. However, what may work for one type of person or personality may not have the same impact on another. This is one of the many areas of managing where learning personality types can be extremely useful.
5) Only giving corrective feedback without any positive feedback – If the only time you give feedback is to say something negative, employees will inevitably develop an automatic defensive reaction the moment you try to give them any type of feedback, whether it be positive or negative. Such conditions can be deemed hazardous for a constructive conversation and effect the overall culture of the workplace.
Some situations in life are just uncomfortable and performance reviews are often one of them. By planning ahead, these conversations can be extremely productive and used to strengthen employee-manager relationships while driving positive outcomes for the business. Set clear expectations, continuously monitor employee performance, regularly check-in, offer praise for good performance and continually work on staff development. You will be well on your way to creating a positive work environment where both parties are appreciated and respected.

Technology continues to create more tools for recruiters to use to reach potential candidates—whether it be via email, social platforms like LinkedIn or the most popular, texting. While texting is an informal way to communicate, it can act as simple way to vet someone to see if they are a good fit for your company or at the very least, see if they are interested—this can be an optimal time saver. The number of technology companies creating messaging tools to help organizations reach potential employees by text continues to grow.
With most nonprofit organizations are constrained by limited bandwidth, utilizing a text-messaging platform could be a beneficial solution that could help bring in the ideal employee while managing time more effectively. Adding this type of tool to your hiring process can help fine tune interview logistics and allow for pre-screening questions prior to scheduling a phone or in-person interview. In such a highly competitive market, nonprofits are always looking for solutions to grab the attention of candidates that are the best fit for the job as well as better manage how they communicate with those seeking an open position.
Compared to email and job board email listings, incorporating text messaging into your recruiting process can increase the likelihood of actually getting a response. Texting offers a quick back and forth conversation, which can help move the process along at a quicker pace, allowing employers to ask basic questions regarding requirements, experience and availability—while candidates can ask about benefits or pay. This could all be discussed before scheduling a meeting or even a phone call—preventing the off chance of wasting either parties’ time. Texting also offers an informal environment that can help decrease the chances of any awkwardness of a first-time discussion.
While text-based recruiting is more commonly used for higher volume job categories such as retail, food service, nursing and customer service, there are some companies using these solutions for professional jobs or high-demand positions such as software programming. These messaging tools are being used to hire a wide-range of positions and continue to become more sophisticated as the demand increases.
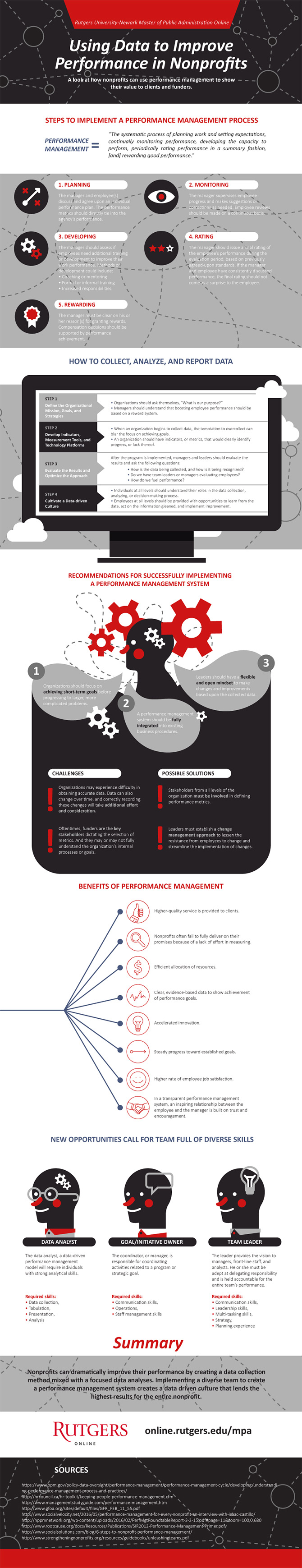
Performance management enables business leaders to motivate staff members and maximize worker productivity. Go-getting employees thrive on productive feedback, while others need a clear plan to boost their productivity.
While large corporations devote huge sums of money toward highly complex and feature-rich performance management software suites, these systems typically focus on standardized forms and universal rating systems. Often, this kind of one-size-fits-all management is unproductive and ineffective. Fortunately, there are newer, cost-effective performance management applications that are accessible to even the smallest organizations that do a better job of boosting performance.
With the abundance of available software suites on the market, small organizations can lease performance management applications for pennies on the dollar. Of course, business leaders must also consider the costs involved with managing these kinds of applications. As such, it makes good sense to choose a management suite that is easy to use and integrates well with existing work processes.
To learn more about how low-budget organizations can effectively achieve their goals through data and performance management, check out Rutgers University’s infographic on Using Data to Improve Performance in Nonprofits.

The role of an HR professional requires wearing many hats and with that comes the challenge of juggling multiple projects, involving various moving parts of a nonprofit organization. One of the biggest and most challenging tasks that lives on the desk of human resource professionals is recruiting/hiring new employees. Most have come to learn that the hiring process has a tendency to be biased, which comes with moments of being unfair to certain applicants. While most of it comes from an unconscious bias, these acts still play an intricate role in making a decision when hiring a new employee.
While bringing awareness to our natural bias and attempting to correct these behaviors can be difficult, there are solutions that can be put into place to offer your human resource’s team a strategic plan to help prevent such biases from occurring.
1) Reformat your job descriptions: A job description is one of the most crucial parts of the hiring process. It sets the tone for everything that follows and the parameters around the type of person you’re looking to hire—from their skills to their capabilities. The use of different words can have a greater impact than you realize on the candidates that come across your job listing. For example, certain adjectives like “competitive” and “determined” can be more appealing to men where as “collaborative” and “cooperative” tend to resonate more with women.
2) Try “blind hiring”: A technique that “blinds” you from seeing any demographic-related information for a particular candidate. This approach can help improve the chances of not weeding out a great candidate and to retain a more dynamic interview pool without your natural bias interfering with the hiring process.
3) Assessments using work examples: Offering a test to solve work-related problems can be a helpful indicator to both the potential hire and employer— revealing their level of job performance and the opportunity for the candidate to demonstrate his or her skill level. This can help eliminate the bias and unconscious judgement of appearance, gender, age and personality.
4) Create a consistent interview process: While an unstructured interview can allow for a more organic conversation, it tends to be unreliable when predicting job success. Whereas in a structured interview, the candidate is asked a set of defined questions, allowing employers to focus on the key factors that have an impact on performance—this approach offers a consistent interview process and minimizes potential bias.
5) Implement goals of diversity: Creating these goals will offer guidance and define the parameters in which to abide by—this helps keep diversity and equality top of mind when hiring future employees.

Question: Can we require our employees to get flu shots?
Answer: While there is no law that prohibits employers from mandating flu shots — and in some states, the law requires all healthcare workers to get flu shots — you should carefully determine if the benefits to your business outweigh the risks. There has been a rise in litigation brought by employees who object to this requirement for medical, religious or personal reasons. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) has filed or joined several lawsuits over claims that inflexible mandatory vaccination policies are discriminatory.
Employees may be entitled to exemptions from a flu shot policy for medical reasons under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or religious reasons under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Requests for exemptions must be evaluated individually yet treated consistently, a difficult task. You will need to engage in an interactive process with the employee, just as you would for any other request for accommodations, to determine if they can be granted without presenting undue hardship to your company.
The EEOC recommends against mandatory flu shot policies, instead suggesting employers encourage employees get vaccinated on their own. Offering no-cost flu shots on site can further improve workplace vaccination rates by making it more convenient for employees.
If you choose to enact a mandatory flu shot policy, write it carefully to protect your company from the risk of discrimination claims and be sure to run it by your legal counsel. Make sure the policy:

With holidays on the horizon, this is the time for holiday shopping, family gatherings and ringing in the New Year. With so much on our plates, time can get away from us—causing us to miss important deadlines. As a 501 (c)(3) organization, November is the deadline month to exercise your state unemployment tax exemption for 2019. This means time is running out.
Unlike for-profit organizations, 501(c)(3) nonprofits have the unique opportunity – as allowed by Federal law – to opt-out of the state unemployment tax system and instead only reimburse the state, if and when they have an actual unemployment claim. It can be a savings opportunity for many nonprofits who have lower claims than what they pay in state unemployment taxes—which are often driven up by for-profit organizations and other companies that go out of business, as well as state fund deficits and improper payments made in error.
UST helps nonprofits to better manage their cash flow through proper claims administration and various funding options. With access to e-Filing capabilities, state-specific claims advice and a plethora of on-demand HR services, UST participants are able to streamline operations and reduce back-office paperwork burdens.
Last year alone, UST helped program participants save $26.2 million in unemployment claims costs. That’s millions of dollars more for the nonprofit sector and the communities they serve.
More than 2,200 of your nonprofit peers are already exercising their unique tax alternative with UST. In a time of such uncertainty and ongoing legal changes, shouldn’t you investigate whether UST can help your organization safeguard valuable time and funding?
Submit your FREE Cost Analysis Formno later than November 15th in order to meet the state deadline for 2019 enrollment – which for most states is December 1st. Unfortunately, if a nonprofit misses the state deadline, they have to wait until the following year to exercise their tax exemption and join the UST program.

Question: If a new hire volunteers information about medical issues, can the employer ask for a doctor’s fit-for-duty certification?
Answer: Exercise caution in requesting medical documentation from applicants or employees, unless the applicant or employee is specifically requesting some form of accommodation in order to do his/her job or the employer has directly observed or has evidence that the employee is having difficulty in the job due to some type of limitation. If the employee discloses the information in the interview and/or onboarding process without a request for accommodation, we recommend the interviewer ask the employee if accommodation is requested. If not, then we recommend moving the conversation on to the bona fide requirements of the job. An employer should consider the following questions before requesting a fitness- for-duty medical certification:
Did the applicant or employee ask for an accommodation? If so, then requesting medical certification and suggestions in order to aid the applicant/employee may be appropriate. Does the employer request this information for all employees/applicants for the same position? If the employer is considering asking for medical certification based upon the new hire’s health disclosure AND the new hire is not requesting any form of accommodation in order to do the job, then we recommend NOT asking for that medical certification unless the employer asks for it for all new hires in that position on a routine basis.
From a practical perspective, an employer should gather medical information only if there are concerns about the employee’s ability to perform the essential functions of the job, considering any physical or mental limitations. An employer should request and consider only the information that is “job related and consistent with business necessity”. Here are a few scenarios where requesting a medical fitness for duty certification may be appropriate:
Q&A provided by ThinkHR, powering the UST HR Workplace for nonprofit HR teams. Have HR questions? Sign your nonprofit up for a free 30-day trial here.

While nonprofit marketing metrics such as engagement, social shares, and “likes” offer insight into your campaigns—other metrics like dashboards, strategic plan reports, financial and activity reports can offer a basic yet sophisticated snap shot of your nonprofit’s overall performance.
As a nonprofit leader, looking beyond the metrics of a simple activity or campaign and focusing on the long-term viability (appealing to users and supporters), relevance and sustainability (access to and use of funds) of your organization as a whole—offers great insight into the performance and longevity of your nonprofit.
Here are some metrics that offer valuable information around the viability and sustainability of your organization:
1) Viability and Engagement:
a) Following the patterns of your users, such as the increase of benefits and engagement.
b) An increase of social media followers, leading to a higher number of content shares.
2) Sustainability and Financial Security:
a) A change in source of funding (i.e., philanthropy, government, fees) followed by observing the strengths and effectiveness of these different funding sources.
b) A change in seeking of funding (i.e., reserves, endowment), and monitoring the status of each request and how successful the outcome is.
Measurement doesn’t just show progress or results—it shows insights and, perhaps most importantly, shapes behavior. The use of these metrics will reveal if your organization has the relevance and viability to encounter current and future challenges and the ability to make necessary adjustments.
If the leadership associated with a mission-driven organization believes strongly in the mission of their nonprofit, they will endure the struggles to establish the long-term viability and sustainability for the organization—ensuring the mission is the number one priority.
Different things inspire different people to work for nonprofit organizations—it can be a personal tie to the cause, the desire to make a difference, the work environment, or maybe, it’s the idea of working with really like-minded people. Whatever the reason is, it typically isn’t for stellar compensation.
While some nonprofits have the funds to offer exceptional compensation, many just don’t—there are a lot of reasons why nonprofit organizations struggle with offering competitive compensation packages but the most common are minimal funding and other spending priorities. We know there are many non-monetary rewards of working for a nonprofit, but creating the best compensation package possible can make the difference between attracting and retaining qualified candidates or suffering from high turnover. It’s important to recognize that nonprofit employers compete with for-profit employers all the time when it comes to finding talented job candidates. Equally important to recognize is that compensation isn’t just about salary.
Like all other employers, tax-exempt charitable nonprofits are required to follow federal and state wage and hour laws that include minimum wage requirements. To maintain their tax-exempt status, nonprofit organizations need to ensure that compensation is reasonable and not in excess. Performing your own data research to find out what the “going rate” is for a given position can be extremely helpful in ensuring that you’re aligned with other nonprofits in the same geographic area with a similar budget and mission.
Here are some things to consider when creating a desirable compensation package:
1 . Incentive Bonuses – Ensure expectations are clear surrounding any bonus through corporate communications that explain how bonuses are recognized as a discretionary gift to a regular salary–dependent upon budget limitations, and provided in recognition of an employee’s extra-efforts or exceptional performance.
2. Work from Home Opportunities – Provide employees the option to telecommute in an effort to save time and money on commuting back and forth from work. Make sure that you have a clear policy surrounding a telecommuting program to avoid any possible issues in the future.
3. Recognition Awards – Recognize employee’s successes on a quarterly basis by rewarding them with an additional perk such as a gift card to a local hot spot or perhaps a paid day off. This type of recognition carries extra meaning in building trust and loyalty.
4. Additional Time off – Offering additional time off options such as a floating holiday or a paid birthday can go a long way in making employees feel valued and cared for.
5. Perks and Memberships – More and more companies are providing their associates free memberships to discounted programs and offering special offers.
6. Increase Training Spending – Consider paying for certification programs, learning materials and conferences. Create more budget space for investing in employees.
Being creative with your compensation package at a budget restricted nonprofit can be less expensive and often better received than a raise, so put on your thinking caps and leave no stone unturned. R emember, money alone will not keep employees engaged so make sure you show them some appreciation.

September resulted in positive job growth with employers adding an additional 134,000 jobs—resulting in an average monthly gain of 201,000 over the past 12 months. These jobs were added across a variety of sectors including professional and business services, health care, transportation and warehousing.
The unemployment rate dropped by 0.2 of a percentage point to 3.7% in September, and the number of unemployed persons decreased by 270,000 to 6.0 million. Over the year, the unemployment rate and the number of unemployed persons declined by 0.5 percentage point and 795,000. The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) showed slight change at 1.4 million in September and accounted for 22.9 percent of the unemployed. Over the year, the number of people employed part time for economic reasons increased by 263,000 to 4.6 million
Job gains occurred in professional and business services (54,000), healthcare (26,000), transportation and warehousing (8,000), construction (+23,000), manufacturing (+18,000), and mining (6,000) while leisure and hospitality showed little change (-17,000). Prior to September, employment had shown an upward trend, however Hurricane Florence might have had an impact on the number of jobs for this industry. Employment in other major industries, including wholesale trade, retail trade information, financial activities and government, showed little to no change over the month.
In September, average hourly earnings for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls increased by 8 cents to $27.24. Over the course of the year, average hourly earnings had risen by 73 cents or 2.8 percent.
With the impact of Hurricane Florence affecting parts of the East Coast during the reference periods in September for the establishment and household surveys, the Bureau of Labor Statistics will be releasing the state estimates of employment and unemployment on October 19, 2018 at 10:00am (EDT).

People get addicted to all sorts of things that aren’t good for them: smoking, drinking, drugs, food. You don’t even need to like something to form an addiction to it—you just need to experience it consistently enough that it becomes your “normal”. We all stress at some point or another and that’s never going to change—it’s just a part of life.
Work related stress somehow makes us feel accomplished and successful. Without the daily rush of adrenaline created by stress, we don’t quite feel like we’ve done enough. This work style has reached epidemic proportions and we don’t need a study to see that. Just listen to the conversations that are happening in your day-to-day surroundings.
If you can answer yes to more than one of the following questions, you are likely addicted to stress and in need of some thoughtful change:
While you are likely doing a fabulous job at getting all the things done that need to be done, the long-term side-effects that unmanaged stress can have on your health can be quite dangerous. The body reacts similarly to stress as it does to drugs and have been shown to have such side effects as elevated blood pressure, increased heart rate, migraines, depression and even loss of brain cells. Unmanaged stress has also been linked to a higher risk of cancer and heart disease—ultimately taking years off our lives. Whatever we experience in our minds eventually manifests itself in the body so it’s important to recognize when you are feeling stressed and make positive changes to ensure you don’t cause yourself long-term health issues.
As with any addiction, the first step in recovery is recognizing that you are addicted. Most addicts know the consequences of their behaviors but simply can’t bring themselves to come down from the adrenaline rush. Many of us thrive on stress—the crunch of a deadline, the nonstop emails that hit our inbox, the countless meetings to prepare for, the list goes on and on. We convince ourselves that with such busy schedules and extreme workloads that there’s no way we can succeed if we slow down. One of the challenges in stress management is fighting our tendency to be pulled back into the adrenaline rush but the good news is that there are ways to break this unhealthy cycle once and for all. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, taking a walk, yoga and massage have all been shown to be quiet effective when done regularly.
Work addiction, often called workaholism, is a real problem and like any other addiction hard to break but if you commit to breaking your addiction to stress at work and take the time to appreciate what you’re working so hard to accomplish, you’ll be more focused, more creative and more productive.

Being on a nonprofit board can require you to wear many different hats and one of the most important aspects of being on a board is learning the budget approval process. Some board members come equipped with a business background—comfortable dealing with budgets and numbers. On the other hand, some may not have the same appreciation or knowledge base when it comes to understanding the financials.
Since each nonprofit organization has a different approach when it comes to handling their budget, there can be some confusion or differences of opinion amongst board members. Educating your board on the proper key terms, types of budgets and the different approaches, is key to ensuring the best decisions are being made on behalf of the organization.
Here are a few key terms to understand when learning the basics of a budget and some specific terms used when discussing nonprofit budgets:
These terms will help your board increase its financial literacy by reducing the mystery of nonprofit budgets, financial reports and auditing. Since a budget plays such a vital role in a nonprofit’s ongoing financial viability, it’s important your board members can fully understand and approve such budgets.

A subsidiary of the California Association of Nonprofits (CalNonprofits) – a statewide alliance of more than 10,000 nonprofits that serves as the voice of the nonprofit community, CalNonprofits Insurance Services (CIS) has been helping California nonprofit organizations with their insurance needs since 1984. Offering exclusive, cost-saving insurance products ranging from general liability coverage to employee benefit programs, more than 900 nonprofit organizations have chosen CIS as their preferred insurance broker.
CalNonprofits Insurance Services has become the one-stop insurance solution for nonprofits in California since its inception and continues to gain momentum. Not-for-profit organizations have unique insurance needs that differ drastically from any for-profit business and CIS understands those needs better than anyone else – constantly researching new products and services to ensure they have solutions to fit whatever benefit needs are out there.
Developing exclusive, cost-effective plans and discount programs that benefit their clients and keeps nonprofits’ insurance dollars at work within the sector is their missions work. “CalNonprofits Insurance Services is unique because we are a social enterprise subsidiary of the California Association of Nonprofits (CalNonprofits),” said Colleen Lazanich, CEO at CIS. “Revenue generated through CalNonprofits Insurance Services stays in the nonprofit sector and strengthens the nonprofit communities in California.”
Dedicated to serving California nonprofit organizations for over 30 years, CIS has the expertise to help nonprofits determine the best insurance coverage needed to protect their unique needs. To learn more about CalNonprofits Insurance Services, visit https://calnonprofitsinsurance.org/!

Competencies are designed to help individuals grow in their roles and their organizations. However, when competencies are poorly defined or applied incorrectly, they can undermine a nonprofit’s talent management process.
According to the Stanford Social Innovation Review, 1 in 4 senior nonprofit executives will leave their organizations within the next 2 years. These departures can result in a loss of productivity and require the use of organizational resources in order to fill the position. The time and energy spent recruiting and looking for a replacement can equal an employee’s salary depending on the position. These retention rates can have an effect on the managerial level as well. Research shows that managers believe that finding employment elsewhere is the only way they will grow faster.
To reduce turnover, nonprofits can create a talent management process that defines and uses competencies that will help individuals grow in their roles and organizations. When defined and used properly, competencies can help identify particular skills, capabilities, and experiences needed for employees to perform at their best and to encourage future growth.
Here are 4 common mistakes nonprofit organizations make when defining and using competencies:
1. To use competencies properly when assessing an individual’s performance.
A performance assessment of an individual should be based primarily on how well they are doing against their agreed upon goals and target for the year. Competencies enable this performance and act as a guide for individuals to understand the skills they need to develop to improve their performance over time. Organizations that do this right use the performance assessment to identify the competencies for each individual to work on.
2. Only thinking of competencies in relation to the work of the individual and organization.
Most nonprofits, that have identified and defined competencies, use a list of job-related competencies. These are generally relevant for everyone in the organization (e.g. communication, dependability, workload management) and can include ones that are specific to certain roles. However, many nonprofit organizations forget that they need to have a set of leadership competencies along with the job competencies — to encourage organizational success.
3. Failing to tailor competencies that are both organization-specific and future oriented.
Some nonprofits have a starter set of competencies that they work with that were either pulled from an HR website or another resource. However, most organizations have not considered if these competencies will enable the organization to achieve strategic priorities. While starter lists provide a good foundation, there needs to be a set of competencies that are specific to their work and encourages future success.
4. Not defining competencies that make them user friendly for development purposes.
While many organizations have a short definition for each competency, only a few have taken the time to create a more elaborate definition for each one. This would provide a better understanding of what it means to progress from an early stage to an advanced stage for each competency.
Nonprofit organizations that approach identifying and using competencies with leadership development in mind avoid many of these pitfalls. In addition, getting the competencies right and using them for development purposes gives nonprofits a better chance at increasing retention and job satisfaction among emerging leaders.

A study by the John Hopkins University Center for Civil Society Studies (@JHUCCSS) has found that nonprofits are a significant and growing source of jobs and economic activity worldwide.
The study, The State of Global Civil Society and Volunteering: Latest Findings from the Implementation of the UN Nonprofit Handbook, found that if both paid staff members and volunteers are counted, nonprofits employ 7.4 percent of the total workforce—on average—in 13 nations for which this information was available.
Furthermore, because nonprofits are growing so quickly, it was found that their economic activity is outpacing that of the national average of economic growth in many of the nations studied.
Does this ring true at your nonprofit and in your community? Does it make a difference? Let us know!
Want more about the findings? Read this overview.
It’s June once again, and for many of you that means the year-end closing of the books on June 30th—which means the AUDITORS will soon be coming!
Presented by Jay Azar, Lindquist, LLP Director of Not-for-Profit Practice Services, this on-demand webinar reveals how your organization can better prepare for the year-end audit and make the process more beneficial for you.
Jay provides expert TIPS on:
Watch the webinar recording today and learn how you can get the most out of your upcoming audit.
This webinar series is part of UST’s efforts to educate the nonprofit sector. For more learning opportunities, tips and legal updates just for nonprofits, sign up for our monthly e-News today!
Thousands of nonprofits have registered to solicit donations but don’t always understand state requirements and whether or not they apply to their organization. This nonprofit-exclusive webinar will explain the essentials of fundraising registration as well as review valuable information meant to help ensure that you’re registered before filing your next Form 990.
Presented by Affinity Fundraising Registration and hosted by Maia Lee, this on-demand webinar highlights crucial details you need to know to raise funds legally in any state with information not found in any book or website. Maia is the Director of Sales & Marketing for Affinity Fundraising with more than 10 years of nonprofit marketing and development experience.
This educational webinar will help you:
For access to more learning opportunities, tips and legal updates just for nonprofits, sign up for our monthly eNews today!

Having recently joined UST as a Marketing Project Specialist, Chelsi is excited to be part of a company that strives to help and be an advocate for nonprofit organizations. While she isn’t currently doing any volunteer work herself, she does donate blood regularly and has already participated in corporate volunteer events during her off hours – I think it’s safe to say she’s a good fit.
Chelsi started dancing competitively at the age of three and stayed active in the dance community for the next ten years. She moved from Utah to California when she was nine and later went on to obtain a degree in Health Administration at CSUN. Before taking a position at UST, Chelsi was a Marketing Specialist within the healthcare arena.
Outside of the workplace, she enjoys living an active lifestyle that includes running, yoga and hiking as well reading, DIY projects and binge watching Netflix. She says she loves to bake and is a die-hard Dodgers fan (tough loss this year). Most of all, she enjoys spending time with family and friends and says her favorite childhood memory was time spent having tea and playing dress up with her Grandmother.
When asked which TV show her life emulates, she answered Gilmore Girls, sharing “Growing up with a single mom, our lives were full of ups and downs but I wouldn’t have had it any other way.” Her favorite holiday is Christmas and apparently she especially loves to bake during the holidays – I guess that means extra holiday pounds for the rest of the team though I don’t think anyone will be complaining.
Help us in welcoming Chelsi to the UST team via Twitter @USTTrust or Facebook @ChooseUST with the hashtag #MeetUSTMondays!
Exit interviews can be an extremely effective tool when done properly. By gathering meaningful information from a departing employee about their experiences with your organization, you can make improvements that could increase retention.
Presented by Glassdoor and hosted by Christopher Lee, this on-demand webinar highlights the proper execution of exit interviews and their impact on the business. Christopher is the HR Manager for Epsilon with more than 10 years of experience helping businesses to meet their goals through employee relations, performance management and organizational development.
You’ll learn why the exit interview is so important, not only for the organization but also for the exiting employee, current personnel and future staff.
Watch the webinar recording today!
Want access to more learning opportunities, tips and legal updates just for nonprofits, sign up for our monthly eNews today!

Utilizing State-Specific Unemployment Claims Administrators, Who Help Protest Unemployment Claims and Attend 100 % of Hearings, UST Participants Save More than $27.8 Million in Unemployment Claims Costs.
Santa Barbara, CA (August 14, 2017) – The Unemployment Services Trust (UST), a program dedicated to helping nonprofits reduce paperwork burdens and protect assets, today announced it has identified $26,219,466.13 in unemployment claims cost savings plus an additional $1,592,247.82 in errors that are refunded to UST participants.
Since 1972, 501(c)(3) nonprofits have possessed the exclusive ability to opt out of the state unemployment tax system and instead pay dollar-for-dollar for their own unemployment claims—as allowed by federal law. UST provides nonprofits the tools they need to exercise their unique tax-exemption status in a safe and cost-effective manner, through dedicated administrative support, e-Filing capabilities and expert claims advice.
UST participants are able to efficiently combat improper unemployment claims, meet important deadlines and prepare for claims hearings by utilizing their state-specific claims representative—helping them to avoid costly penalties while offsetting the administrative headache. UST’s claims administrator equips more than 2,200 participating nonprofits with the guidance and resources they need to confidently manage their claims process.
“In a sector where employee bandwidth and funding is often stretched, it’s beyond rewarding to know that UST provides such significant savings to our nonprofit members,” says Donna Groh, Executive Director of UST. “We know this money filters right back into the nonprofit community and that’s what the UST program is all about—strengthening nonprofits’ missions.”
501(c)(3) nonprofit employers with 10 or more employees can submit a free Unemployment Cost Analysis form to readily determine whether their organization is overpaying in state unemployment taxes. Those who enroll in the UST Program will receive instant access to expert claims advice.

PT Barnum’s quote, “There is no such thing as bad publicity” is not the case when an employee comes forward with a claim of harassment or hostile work environment and, to make matters worse, discusses the company’s handling of the situation on social media or in the press.
If you’re a company like Uber, you can hire the former Attorney General to manage the issue. But if you’re not, what can you do to get things under control? And how could your company have avoided the issue to begin with?
Presented by ThinkHR, this on-demand webinar highlights the latest best practices and tools to prevent harassment and discrimination claims.
You’ll learn the key components of respectful workplace cultures for prevention as well as practical ideas for conducting investigations into claims of improper conduct to help resolve issues when they arise.
Watch the webinar recording today!
This webinar offers 1 HRCI and SHRM-approved credit. Want access to more HR-certified webinar opportunities and a live HR hotline? Visit www.chooseust.org/thinkhr/ to sign up for a FREE 30-day trial of the UST HR Workplace, powered by ThinkHR.
The Unemployment Services Trust has added a new eBook to its library, aimed at helping nonprofit organizations to more effectively find, develop and retain the right kind of talent.
SANTA BARBARA, Calif. (September 28, 2017) – The Unemployment Services Trust (UST) reveals some of the most common courses of action to take in order to help sustain employee talent that’s a best-fit for organizational values, culture and mission. This short eBook provides ideal tactics nonprofits can utilize when approaching reoccurring struggles with recruiting and retaining personnel.
As a nonprofit organization, having the right team is critical to your mission. Without the guidance of strong and steady leadership or the driving force of sufficient organizational support, nonprofits are left vulnerable to financial, strategic and geopolitical uncertainties.
The eBook, “Nonprofit Talent Sustainability Strategies: 5 Ways to Combat Hiring & Succession Planning Obstacles,” reveals that “77% of nonprofit organizations across the country have no leadership transition or a succession plan.” Such lack of preparation can lead to staff burnout, unfinished projects, lost deadlines, and unrealized mission goals.
“The competition for talent is at an all-time high, making it essential that your organization understands how to leverage the benefits you have to offer,” explains Donna Groh, Executive Director. “This eBook provides the insight organizations need to best prepare for inevitable staffing departures while persuading stellar job candidates to come onboard—helping them save valuable time and money.”
Utilizing recent survey data and nonprofit employment trends, UST is able to provide nonprofits with the top five ways to combat hiring and succession planning obstacles.
The eBook, now available for free download, also highlights:
You can download your complimentary copy today at: http://www2.chooseust.org/2017/eBook

UST maintains a secure site. This means that information we obtain from you in the process of enrolling is protected and cannot be viewed by others. Information about your agency is provided to our various service providers once you enroll in UST for the purpose of providing you with the best possible service. Your information will never be sold or rented to other entities that are not affiliated with UST. Agencies that are actively enrolled in UST are listed for review by other agencies, UST’s sponsors and potential participants, but no information specific to your agency can be reviewed by anyone not affiliated with UST and not otherwise engaged in providing services to you except as required by law or valid legal process.
Your use of this site and the provision of basic information constitute your consent for UST to use the information supplied.
UST may collect generic information about overall website traffic, and use other analytical information and tools to help us improve our website and provide the best possible information and service. As you browse UST’s website, cookies may also be placed on your computer so that we can better understand what information our visitors are most interested in, and to help direct you to other relevant information. These cookies do not collect personal information such as your name, email, postal address or phone number. To opt out of some of these cookies, click here. If you are a Twitter user, and prefer not to have Twitter ad content tailored to you, learn more here.
Further, our website may contain links to other sites. Anytime you connect to another website, their respective privacy policy will apply and UST is not responsible for the privacy practices of others.
This Privacy Policy and the Terms of Use for our site is subject to change.
UST maintains a secure site. This means that information we obtain from you in the process of enrolling is protected and cannot be viewed by others. Information about your agency is provided to our various service providers once you enroll in UST for the purpose of providing you with the best possible service. Your information will never be sold or rented to other entities that are not affiliated with UST. Agencies that are actively enrolled in UST are listed for review by other agencies, UST’s sponsors and potential participants, but no information specific to your agency can be reviewed by anyone not affiliated with UST and not otherwise engaged in providing services to you except as required by law or valid legal process.
Your use of this site and the provision of basic information constitute your consent for UST to use the information supplied.
UST may collect generic information about overall website traffic, and use other analytical information and tools to help us improve our website and provide the best possible information and service. As you browse UST’s website, cookies may also be placed on your computer so that we can better understand what information our visitors are most interested in, and to help direct you to other relevant information. These cookies do not collect personal information such as your name, email, postal address or phone number. To opt out of some of these cookies, click here. If you are a Twitter user, and prefer not to have Twitter ad content tailored to you, learn more here.
Further, our website may contain links to other sites. Anytime you connect to another website, their respective privacy policy will apply and UST is not responsible for the privacy practices of others.
This Privacy Policy and the Terms of Use for our site is subject to change.
Whether intentional, or unintentional, only 5 percent of those who were screened by Lexis Nexus Risk Solutions had ever been involved in any kind of criminal activity. But more than 1-in-5 of those who had a criminal background had been convicted of serious charges, including drug-related offenses, sexually-based crimes, kidnapping, and murder.
Nearly 1,200 nonprofit employees who were given background checks during the study had been convicted of murder. There were also 600 kidnapping offenses included in the audit.
Every year, Lexis Nexus combines forces with thousands of nonprofit agencies across the United States to conduct background checks and gather information designed to better protect nonprofit organizations in the event of a bad, or worse, accidental, criminal hire.
New EEOC Guidance May Soon Change This
In April, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunities Commission approved new guidance on criminal background checks that requires all employers to individually assess whether an applicant’s past criminal conduct is job related or consistent with business necessity before throwing them out of the hiring pool.
For nonprofits who have encountered problems with employees whose criminal background prove not so distant, and for those who protect clients from criminals, the new rules will be jarring because the EEOC provides only 2 circumstances in which an employer can meet the “job related and consistent with business necessity” on a consistent basis. The first occurs when an employer is able to validate the criminal conduct screen for the position in question. This can only be done in accordance with the Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures Standards if the data about the candidates’ criminal conduct, as related to their work performance, is available and can be validated.
The second, more time consuming and personal, option requires that a nonprofit employer must develop a targeted screen of all applicants considering the nature of their crimes, the time elapsed, and the nature of the job available. The employer must then provide applicants excluded by the screen the chance for an individual assessment to determine whether the policy, as-applied, is job related and consistent with business necessity.
The individual assessment would further require that the candidate is notified that they have been excluded from consideration because of a criminal conviction. According to the EEOC, the notice would have to include an opportunity for the screened candidate to demonstrate that the exclusion should not be applied based on the particulars of the candidates’ circumstances.
The employer must also consider their appeal with merit to the particular circumstances that are revealed during the consideration period.
What It All Means
Thankfully, the same study that found that only 5 percent of those employed by nonprofits have criminal backgrounds found that the number of nonprofit employees with criminal backgrounds has declined for five consecutive years, dropping from 7 percent in 2007 to 5.3 percent in both 2010 and 2011.
According to the study, which is called The Power of Positive Information, “The results… demonstrate that our background screening programs are working for nonprofits and underscore the importance of continued screening vigilance at nonprofits since nearly one-fourth of the records included in the audit were for serious offenses.”
More importantly, the study shares several best practices and program recommendations including:
To learn more about the study or how you can better improve the security of your nonprofit, visit http://www.lexisnexis.com/nonprofit for the full study.